Russian Mobile Game Market
Overview
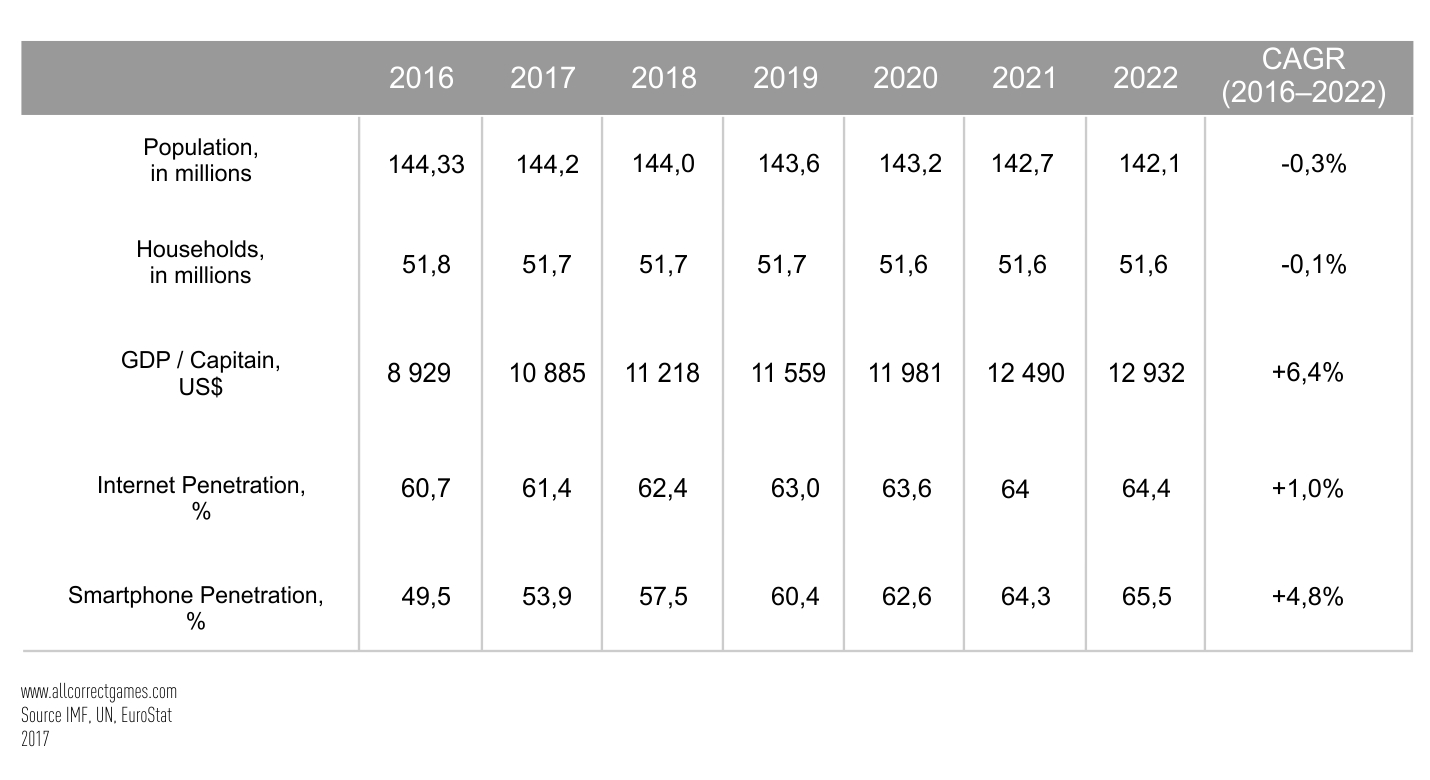
Russia (the Russian Federation, RF) is the largest country in terms of size and the ninth in terms of population. Russia has 85 federal subjects. The distance from the east to the west of the country is almost 10,000 km, and the time difference between the easternmost and westernmost regions is 10 hours.
More than 200 ethnic groups live in Russia, the majority of the population is Russian (80.9%), and there are also Tatars, Ukrainians, Bashkirs, Chuvash people, etc. The official language is Russian; however, republics within the Russian Federation are entitled to establish their own official languages (in this case, Russian must be used in official institutions).
Russia ranks sixth in the world in terms of GDP adjusted for PPP and twelfth in terms of nominal GDP; however, the dynamics of the purchasing power of the country’s population are negative. After the collapse of the USSR in 1991, the economy fell into deep decline due to the rapid transition from a planned system to a market system. In the first decade of the 21st century, well-being among the population improved and the economy reached a stable state. The most important branches of the Russian economy are mining, manufacturing, trade, transport, and communications.
Russia is a multicultural country. Modern culture is based on restoring the traditions of the Russian Empire. In ethnic communities, the practice of maintaining ethnic traditions is widespread. In addition, Western and Eastern civilizations have a strong influence.
Mobile Games Market in Russia
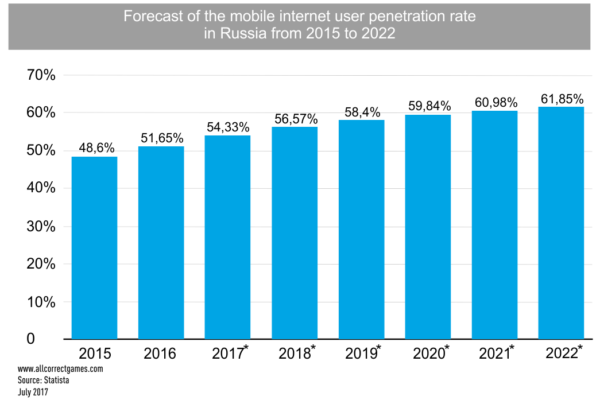
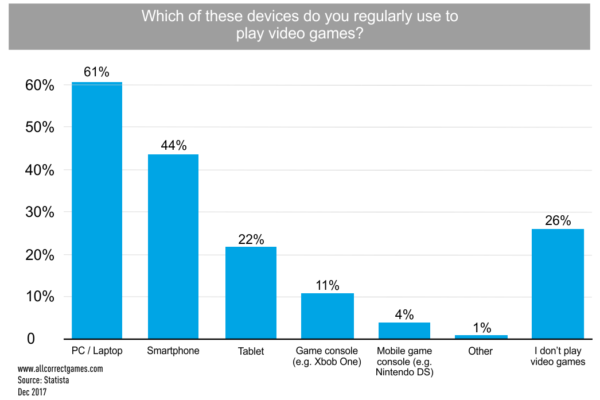
According to data of 2016, more than 70% of Russian citizens use smartphones, and more than 50% actively use mobile internet functions. Smartphones are in second place among devices used to play games — 44% of players indicated that they use their phones for games.
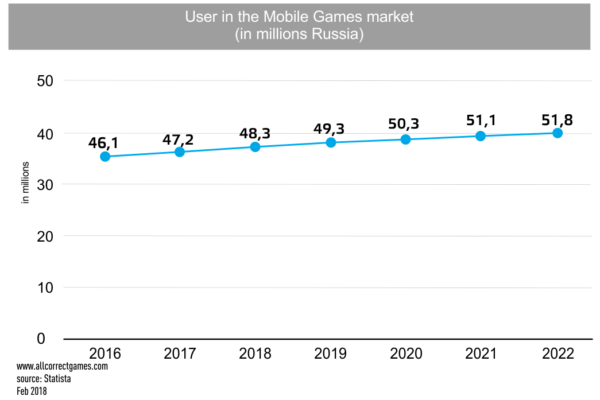
According to data from NewZoo, there are a total of 71.3 million gamers in Russia, of which 47.2 million prefer to play mobile games. The market is still in the growth stage, so the number of players is increasing every year, and is projected to rise to 51.8 million by 2022. This is due both to the increase in the number of smartphones and the affordability of mobile internet: the average transfer cost of 1GB of data is about $1 (in Japan, for example, 1GB costs approximately $8).
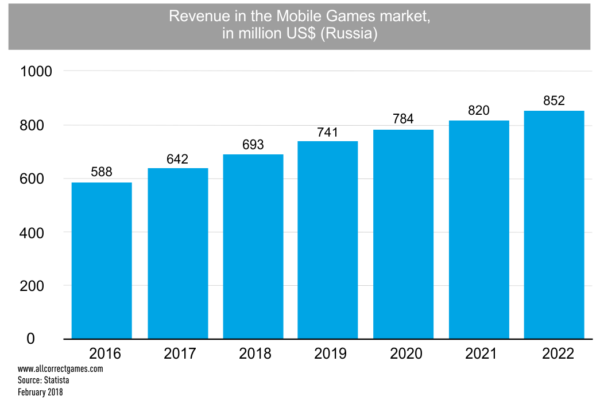
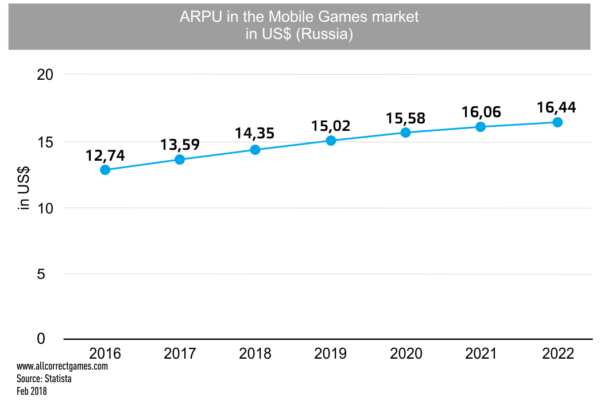
The revenue of companies in the mobile games market is also growing year by year. In 2015, the market dynamics in dollar terms declined sharply due to the depreciation of the ruble; however, in 2016, the situation was partly rectified due to changes in the business models of developers, and partly because of users adapting to the new conditions.
Russian players do not really like to pay in games — ARPU is $13.59. At the same time, expenditure on promoting games is also not high — according to data from Chartboost, the average CPI for June 2018 was $0.44 for Android and $1.03 for iOS.
According to data from AppAnnie, Russia is the leader in terms of the number of downloads of mobile applications among European countries. In the world market, it is overtaken by China, the US, India, and Brazil. However, users prefer not to buy applications, opting instead for free versions.
Who plays mobile games in Russia?
In Russia, there are 47.2 million active users of mobile games, and according to data from Statista, this figure is set to rise. This is due to the increasing prevalence of smartphones and mobile internet. In addition, the age boundaries of the segment are widening: 71% of children aged 3–10 play mobile games. Many parents are encouraging games with enriching content and even play them with their children.
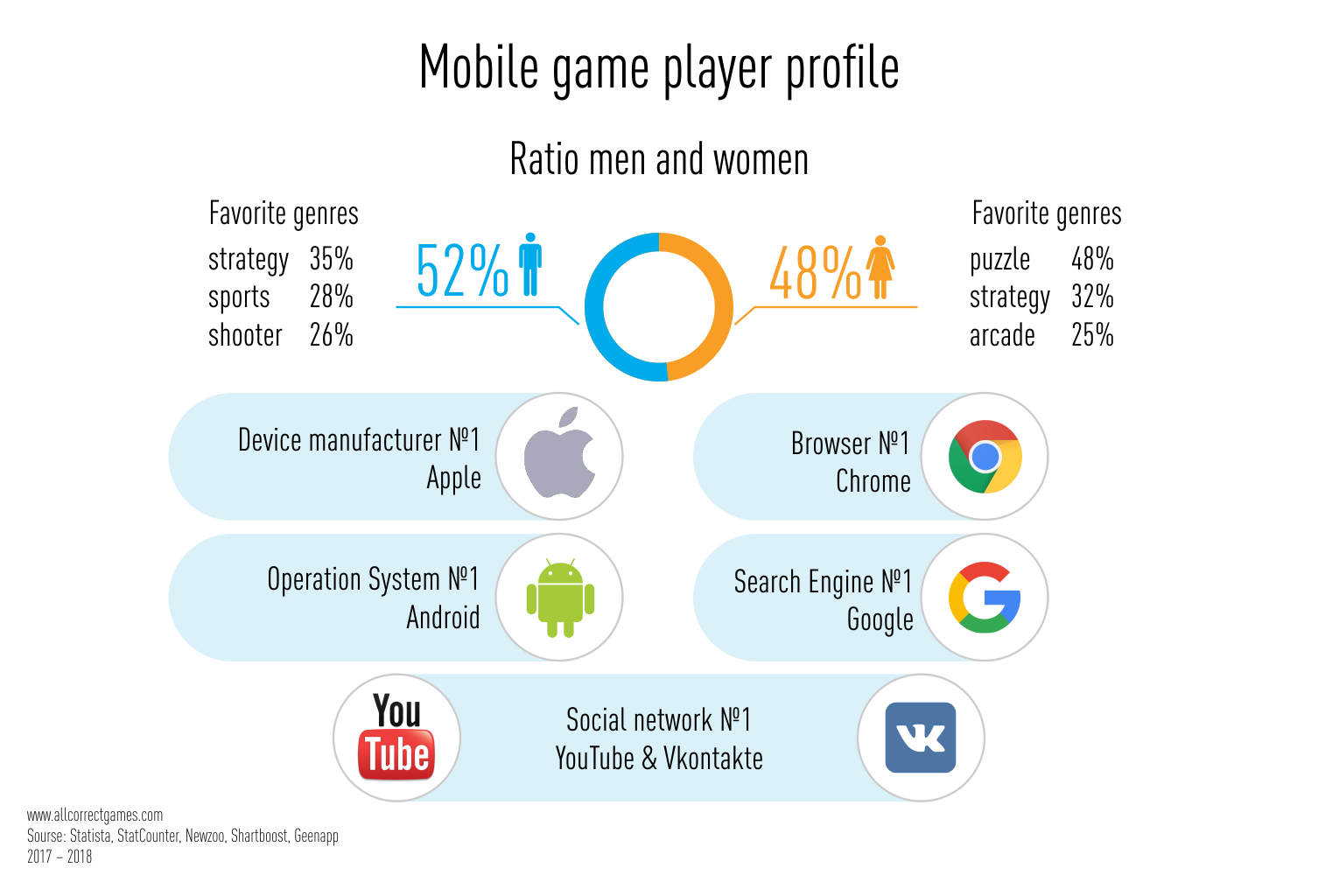
As expected, the segment that pays the most are gamers who are 25–35 years old. Players under the age of 24 bring developers up to 30% of their profits. Most payments are made in the first few days after an application is installed.
On the Russian market, 52% of users are men and 48% are women. Men prefer strategy games, sports simulators and shooters, and women prefer puzzle, strategy, and arcade games. Women play games more often, more than 5 days a week, but men pay more — 48% of men are willing to pay for game content compared to only 32% of women.
Users prefer Apple (32.03%) and Samsung (24.94%) devices. There are significantly more Android users than iOS users — 65.46% against 32.03%. The most popular browser for mobile OS users is Chrome (preferred by 48.78% of users).
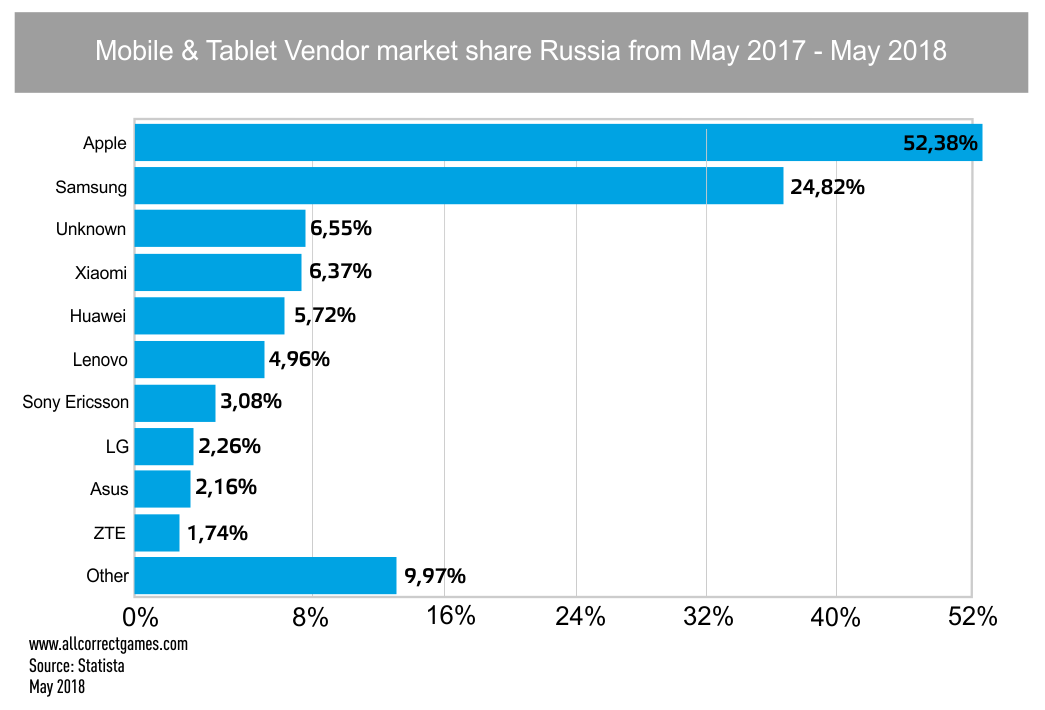
According to Statista, the most popular social networks in Russia are YouTube and VKontakte. For messaging, people prefer to use Skype or WhatsApp. Among search engines for mobile internet users, Google is in the leading position (53.18%); however, the local Yandex is only slightly behind the global giant (45.03%).
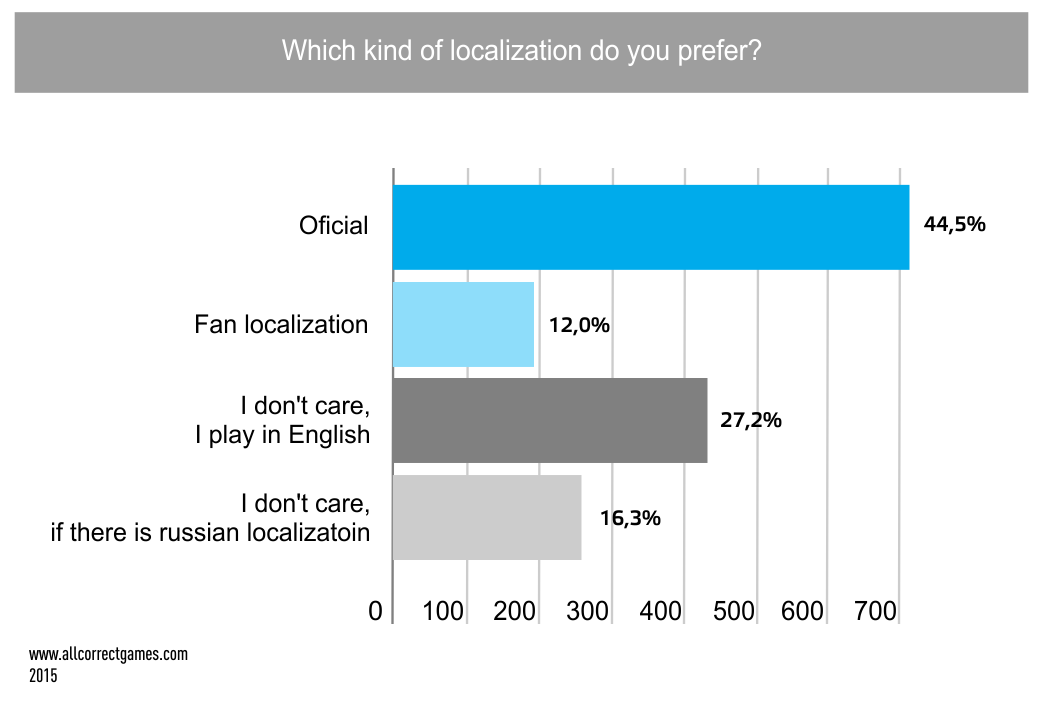
Russian players are rather demanding when it comes to translations. According to a study conducted by Allcorrect Games, most players prefer to play either fully translated games (in-game text and voice-overs), or partially translated games (in-game text and subtitles).
Russian mobile game developers
Among the top developers earning on the Russian market, there are companies from a wide range of countries: Israel, Finland, Lithuania, Turkey, China. One of the Russian developers that makes the top ten is Playrix (the company’s head office is in Ireland, but production is concentrated in Russia). This company also features in the global rating of mobile developers and ranks 32nd.
According to AppAnnie, the top ten main developers on the mobile games market in Russia for July 2018 are:
- Playrix
- Playkot
- TAPCLAP
- RS Technologies
- Kefir
- Pixonic
- Nekki
- Incrdbl
- Overmobile
- ZeptoLab
It is worth noting that the games industry in Russia is developing rapidly. In 2016, developers’ revenue increased by 54% compared to 2015. Growth in the online games market was only 9%. The reason for this is the stage of growth that the mobile games segment is currently in and also the affordability and prevalence of devices.
Culturalization for the Russian population
Russia is a multinational and multicultural country, therefore it is rather difficult to find a single “cultural code” that will be understood equally by all. Nevertheless, when adapting a game for Russia, it is worth taking a number of things into consideration.
- Despite the fact that people in Russia sometimes criticize the country’s position in the international arena and the actions of the government, they do not take well to criticism from the outside. This phenomenon was even described in the early 19th century by Alexander Pushkin: “Of course I despise my fatherland from head to toe — but I’m annoyed when a foreigner shares this feeling with me.”
- Russians are passionate about their native language and prefer to play games that have been translated. However, the Russian language is rather complicated and many words have several meanings. For example, an innocent light blue color or a cockerel will be associated with the homosexual community.
The official national symbols of Russia are the national anthem, the coat of arms (the two-headed eagle), and the flag (the white-blue-red tricolor). When talking about Russia, people often mention another trio: vodka, matryoshka dolls, balalaika. However, these symbols are more likely popular for tourists who visit Russia, rather than the people who live there. In fact, nobody rides through the streets on bears, children don’t assemble nuclear bombs in arts and crafts class, and you are not very likely to find KGB workers in every family — the organization ceased to exist in 1991.
In recent years, Russian legislation has become stricter in terms of requirements for publicly distributed content. What may be prohibited?
- The depiction of same-sex relationships (officially only propaganda of these relationships is prohibited, but almost any manifestation of homosexuality can be applied to this) FZ (Federal Law) No. 436
- Insulting the feelings of religious believers. The difficulty here is that the law has no clear definition of what may be considered an insult, therefore it is best to avoid strong religious themes FZ No. 136
- Describing methods of suicide and calls to commit suicide Order of Roskomnadzor (Federal Service for Supervision of Communications, Information Technology and Mass Media) No. 639
- Nazi symbolism is restricted FZ No. 195
- If your game is intended for children, you should avoid any images of alcoholic drinks or smoking accessories FZ No. 436
- Gambling is prohibited in the Russian Federation (except for four specially organized zones) FZ No. 224
- If mentioning ISIS (a terrorist organization that is prohibited in the Russian Federation), it must be stated that the organization is prohibited within the Russian Federation.
Despite the fact that the USSR collapsed more than 25 years ago, there is still a strong Soviet legacy in Russia. People are sensitive to events such as victory in the Great Patriotic War or the flight of Yuri Gagarin into space. However, attitudes to the Soviet government are ambiguous: some look back on it with nostalgia, others see it as Russia’s worst period in history.
In 2016, the Expert Council of the Gaming Industry was created. Its main focus is to support young Russian developers; however, one of its main goals is to expand international relations. Council members give advice to developers and conduct industry research.
In general, Russian culture tends toward Western culture: people try to keep up to date with modern technologies; they listen to Western music and watch Hollywood films, and they follow Western fashion trends. At the same time, many liberal values are rejected by Russian people. The interest in the East is mainly to do with consuming works of culture (music, books, films, games, anime) and using technology developed in the East.
Localization into Russian
Russian is the sixth most spoken language in the world. There are around 260 million speakers. In addition to Russia, the language is common in CIS countries (in Belarus, Kazakhstan, and Kyrgyzstan it is the second official language), and also in Eastern Europe. It is one of the six working languages of the UN and UNESCO.
In different regions of Russia, dialects may vary slightly, but people speaking different varieties of the language can easily understand each other. The main differences are in the pronunciation of sounds. People living in the north of Russia emphasize the main [o] in unstressed words; the speech of people in the south is distinguished by the fricative sounds [γ] and [х].
The Russian language is based on Russia-specific vocabulary. Many of the borrowed words have Greek, Turkic, and later Dutch, French, German, and English origins. Variable stress is a distinctive feature of the Russian language. The writing system is based on the Cyrillic alphabet.
When localizing into Russian, it is important to remember that the average word length in Russian is 7.2 symbols, while in English it is 5.2 symbols, and when translating from Chinese, one character can become several words. It may be useful to take this into account when developing interface elements.
Useful links
- 75% of Russian mobile phone users are also gamers – 18% make app purchases
- NewZoo — Russian Games Market
- NewZoo — Russian Market Is the 11th Largest Games Market in the World
- Zorka.Mobi — Mobile Gaming in Russia
- Research of the global and Russian gaming market, 2016
- Report: Russia is among the most attractive markets for mobile game marketing