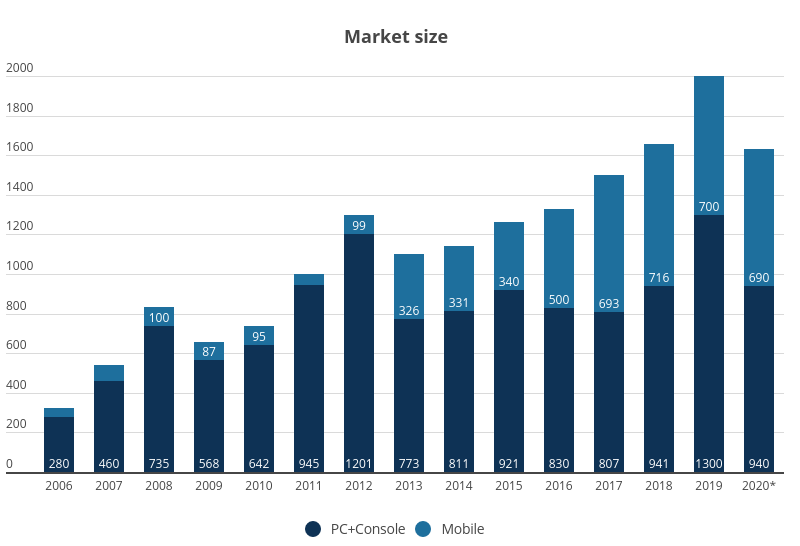
The Russian games market continues to remain geared towards the PC as the primary platform. With the exception of 2017 when the throne was briefly usurped by the mobile games market, PC games have been enjoying their supreme reign over the Russian market since way back in 2006, according to our data.
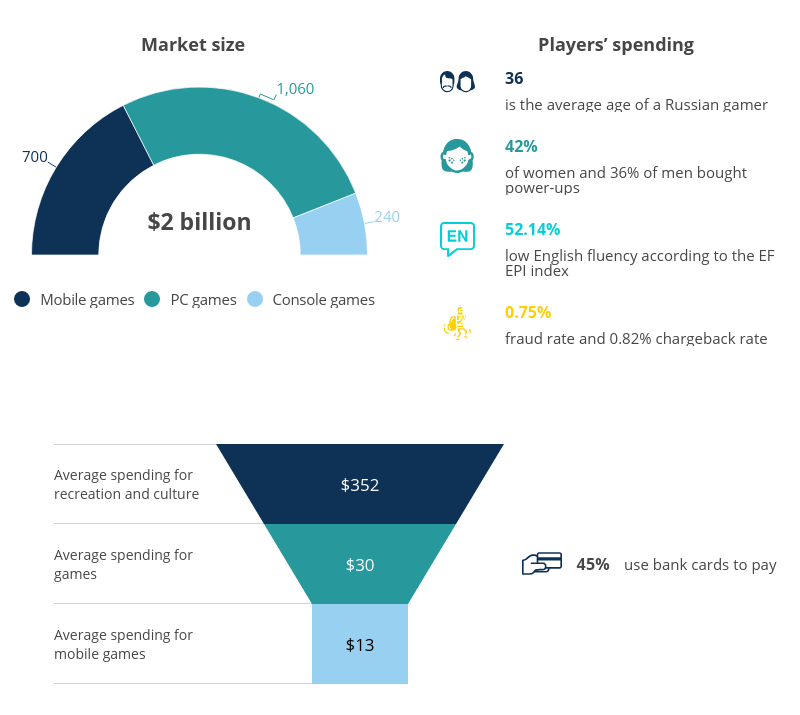
Newzoo reports that the volume of the Russian games market in 2019 reached a new milestone of 2 billion US dollars (Superdata had actually forecast these figures to reach as high as USD 2.7 bln). On the other hand, Newzoo statistics also suggest that the Russian mobile games market either remains stable or is declining. Perhaps this can be explained by the fact that smartphone sales haven’t been increasing at all in Russia — everyone who had been planning on buying themselves a fancy gadget has already done so. The major share of the PC segment profits comes from the so-called nominally free-to-play releases with World of Tanks leading the charge.
This year we didn’t just prepare an analysis of the state of the market in 2019, but we also pieced together a forecast for 2020. According to the data we have compiled, the crises have had a fairly strong impact on the Russian games market, primarily because of the depreciation of the ruble. As a rule, the volume of the market eventually bounces back to the previous year’s figure, marginally compensating for the decline. 2009 saw a boom in social gaming, while in 2013 the mobile game segment experienced substantial growth. Both of these factors combined compensated partially for the depreciation of Russia’s national currency.
Are there any growth factors to consider for the Russian games market in 2020?
First of all, there is always the probability of a successful launch of several new titles, but the market’s main recovery anchor this time lies in the boom of hypercasual mobile games. Considering the insubstantial average spending figures on games, the ad monetization model of hypercasual projects, and the expected decline in personal income, it is extremely unlikely that mobile games will become the main driving force of the Russian market in 2020. Moreover, analysts do not foresee a busier release schedule for hypercasual projects in Russia, which is different to Germany and other countries.
Taking all these factors into account, we believe that the volume of the Russian games market in 2020 will equate to approximately USD 1.6 bln.
PLAYER STATISTICS
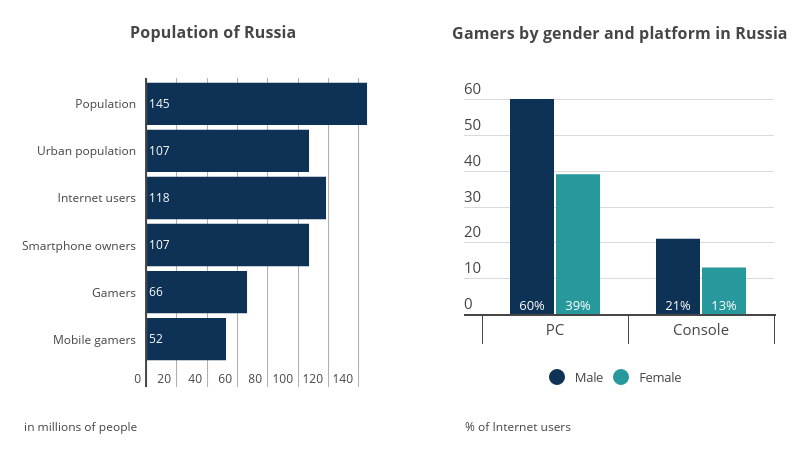
The opinions of analytical companies Newzoo and Superdata differ not only in their estimations of the Russian games market volume but also in their analyses of the players’ habits. Newzoo attests that out of 66 million gamers, 60% are men and 40%, women. The Superdata report, on the other hand, suggests that these figures are at 52% and 48% respectively. The median age of a Russian player is 36 years old (Newzoo), while the average age is 37 years. According to Yandex.Money and Newzoo, 45% of the players pay for games by card. Superdata claims that 26% of the players use the ubiquitous in Europe and the US PayPal, as well as local online payment systems such as Yandex.Money, WebMoney, and Qiwi Wallet, or pay with cash through specially designated terminals and kiosks. Moreover, the percentage ratio of the amount Russian players spend on games to how much they spend on cultural entertainment is equal to that in European countries.
According to Superdata, Russian players spend more time playing limited-time in-game events, trying to earn special rewards. They also prefer purchasing cheap packs that contain either premium currency or additional in-game content.

Russian players are also rather demanding when it comes to translated text. According to a study conducted by Allcorrect, most players prefer to play either fully translated games (in-game text and voice-overs) or partially translated games (in-game text and subtitles).
RUSSIAN MOBILE GAME DEVELOPERS
Among the top developers making a profit in the Russian market, there are companies from a wide range of countries such as China, Israel, Finland, Lithuania, and Turkey. Among the Russian developers that rank in the top ten is Playrix (the company’s head office is located in Ireland, but production is based in Russia).
Developers:
- Playrix
- com
- 1С
- Innova
- Nexters
- Pixonic
- Mytona
- Kefir!
- 101XP
- Game Insight
CULTURALIZATION FOR THE RUSSIAN POPULATION
Russia is a multinational and multicultural country, therefore it is rather difficult to find a single “cultural code” that will be understood equally by all. Nevertheless, when adapting a game for Russia, it is worth taking a number of things into consideration.
- Despite the fact that people in Russia sometimes criticize the country’s position in the international arena and the actions of the government, they do not take well to criticism from the outside. This phenomenon was even described in the early 19th century by Alexander Pushkin: “Of course I despise my fatherland from head to toe — but I’m annoyed when a foreigner shares this feeling with me.”
- Russians are passionate about their native language and prefer to play games that have been translated. However, the Russian language is rather complicated and many words have several meanings. For example, an innocent light blue color or a cockerel will be associated with the homosexual community.
The official national symbols of Russia are the national anthem, the coat of arms (the two-headed eagle), and the flag (the white-blue-red tricolor). When talking about Russia, people often mention another trio: vodka, matryoshka dolls, balalaika. However, these symbols are more likely popular for tourists who visit Russia, rather than the people who live there. In fact, nobody rides through the streets on bears, children don’t assemble nuclear bombs in arts and crafts class, and you are not very likely to find KGB workers in every family — the organization ceased to exist in 1991.
In recent years, Russian legislation has become stricter in terms of requirements for publicly distributed content. What may be prohibited?
- The depiction of same-sex relationships (officially only propaganda of these relationships is prohibited, but almost any manifestation of homosexuality can be applied to this) FZ (Federal Law) No. 436
- Insulting the feelings of religious believers. The difficulty here is that the law has no clear definition of what may be considered an insult, therefore it is best to avoid strong religious themes FZ No. 136
- Describing methods of suicide and calls to commit suicide Order of Roskomnadzor (Federal Service for Supervision of Communications, Information Technology and Mass Media) No. 639
- Nazi symbolism is restricted FZ No. 195
- If your game is intended for children, you should avoid any images of alcoholic drinks or smoking accessories FZ No. 436
- Gambling is prohibited in the Russian Federation (except for four specially organized zones) FZ No. 224
- If mentioning ISIS (a terrorist organization that is prohibited in the Russian Federation), it must be stated that the organization is prohibited within the Russian Federation.
Despite the fact that the USSR collapsed more than 25 years ago, there is still a strong Soviet legacy in Russia. People are sensitive to events such as victory in the Great Patriotic War or the flight of Yuri Gagarin into space. However, attitudes to the Soviet government are ambiguous: some look back on it with nostalgia, others see it as Russia’s worst period in history.
In 2016, the Expert Council of the Gaming Industry was created. Its main focus is to support young Russian developers; however, one of its main goals is to expand international relations. Council members give advice to developers and conduct industry research.
In general, Russian culture tends toward Western culture: people try to keep up to date with modern technologies; they listen to Western music and watch Hollywood films, and they follow Western fashion trends. At the same time, many liberal values are rejected by Russian people. The interest in the East is mainly to do with consuming works of culture (music, books, films, games, anime) and using technology developed in the East.
LOCALIZATION INTO RUSSIAN
Russian is the sixth most spoken language in the world. There are around 260 million speakers. In addition to Russia, the language is common in CIS countries (in Belarus, Kazakhstan, and Kyrgyzstan it is the second official language), and also in Eastern Europe. It is one of the six working languages of the UN and UNESCO.
In different regions of Russia, dialects may vary slightly, but people speaking different varieties of the language can easily understand each other. The main differences are in the pronunciation of sounds. People living in the north of Russia emphasize the main [o] in unstressed words; the speech of people in the south is distinguished by the fricative sounds [γ] and [х].
The Russian language is based on Russia-specific vocabulary. Many of the borrowed words have Greek, Turkic, and later Dutch, French, German, and English origins. Variable stress is a distinctive feature of the Russian language. The writing system is basedon the Cyrillic alphabet.
When localizing into Russian, it is important to remember that the average word length in Russian is 7.2 symbols, while in English it is 5.2 symbols, and when translating from Chinese, one character can become several words. It may be useful to take this into account when developing interface elements.
ALLCORRECT GAME LOCALIZATION STUDIO
Localizing a game into the main languages increases its revenue by a factor of 1.9 (based on data from Google Europe and Allcorrect’s research).
Allcorrect is an ROI-based localization company. Our approach is based on finding profitable markets for developers and publishers and adapting games for target audiences, taking particular cultural aspects into account. Our goal is to make your games popular and your players happy.
We’ve been translating games since 2008, and we’ve localized over 968 projects during that time. Our portfolio includes localizations of large-scale AAA projects as well as indie games that have dominated the international market.



